AP FEMUR PROJECTION
Anteroposterior • Complete view • Evaluation of the longest bone in the body
Exposure Factors
Standard exposure: Parameters for optimal visualization of femoral bone
Anatomical Structures Visible
Should be clearly observed:
- Complete femur - Longest bone in human body
- Femoral head - Proximal portion
- Femoral diaphysis - Body of femur
- Femoral condyles - Distal portion
- Trochanters - Greater and lesser
- Femoral neck - Subcapital region
Joint inclusion criteria:
Ideal technique: Include both joints when possible for complete evaluation
Cassette Size and Orientation
Longitudinal orientation to cover the complete femur from hip to knee
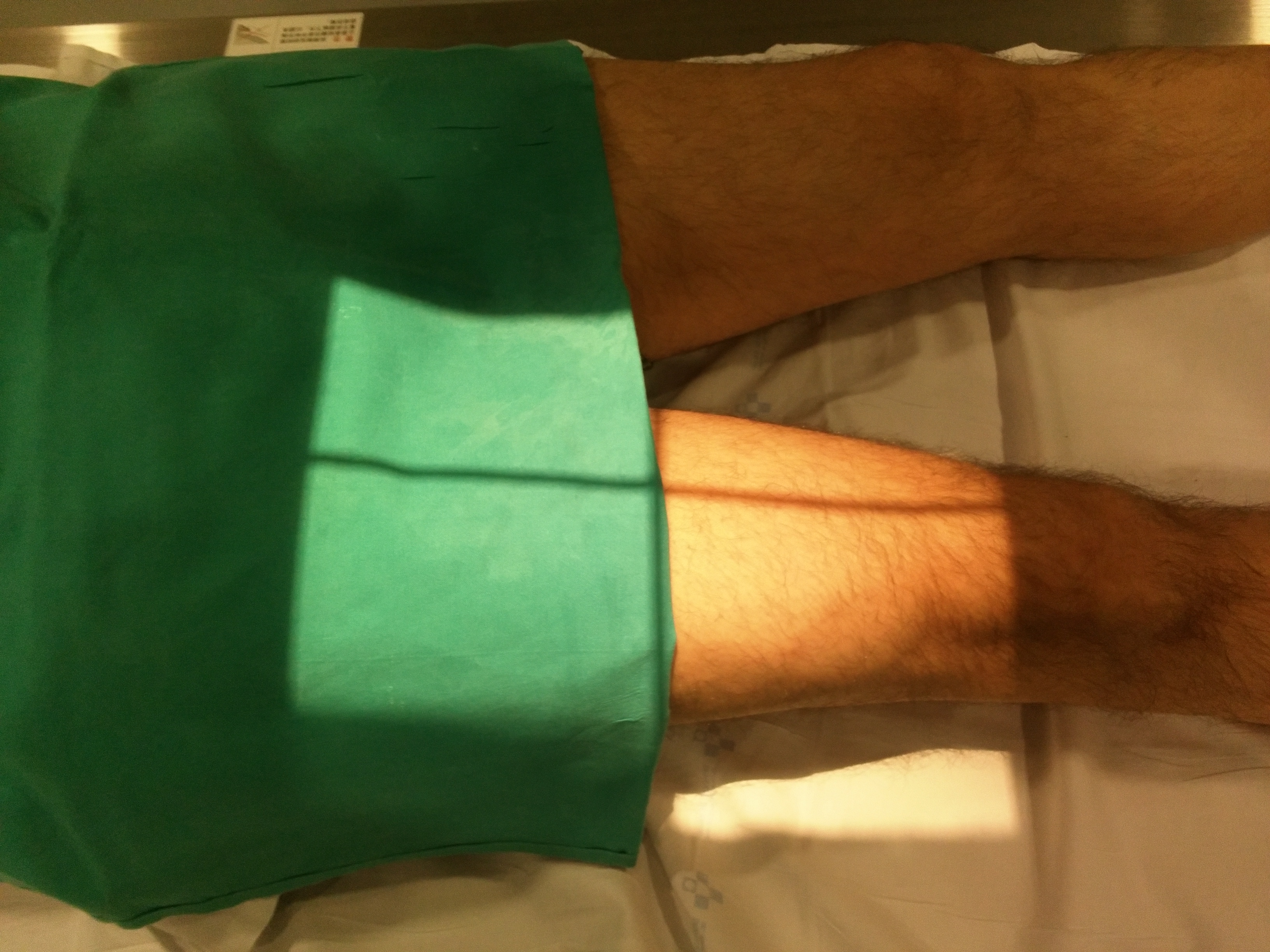
Patient Positioning
VARIATIONS ACCORDING TO AREA OF INTEREST
PROXIMAL
Includes: Complete hip
Centering: More toward hip
Indication: Femoral neck fractures
MIDDLE
Includes: Complete diaphysis
Centering: Center of thigh
Indication: Diaphysis fractures
DISTAL
Includes: Complete knee
Centering: More toward knee
Indication: Supracondylar fractures
Central Ray Point
Without known location: Center of thigh
With known location: Proximal or distal deviation according to interest
Joint inclusion: Adjust centering to include hip and/or knee
Angulation: 0° - Direct vertical perpendicular to thigh
Optimal Image Characteristics
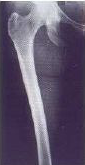
Complete Femur
Longest bone fully included
Hip Joint
If proximal zone included
Knee Joint
If distal zone included
Proper Rotation
Neck visible without superposition
Sharp Details
Cortical and trabecular bone
No Superposition
Contralateral thigh abducted
Common Technical Challenges
Frequent problems in AP femur projection:
- Insufficient joint inclusion - Not showing hip or knee
- Inadequate rotation - Femoral neck not visible
- Superposition from contralateral thigh
- Patient movement during exposure
- Incorrect centering cutting important areas
- Insufficient penetration in obese patients
Solution: Ensure proper abduction of contralateral leg, slight medial rotation, adequate centering
Special Considerations
Trauma Patients
If patient cannot rotate leg, perform in neutral position and document limitation.
Obese Patients
Increase kV and mAs according to thickness, use compression if possible.
Postoperative
Include entire prosthesis or osteosynthesis material in field.
Patient Instructions
"Remain still during the examination"
Avoid any leg movement during radiographic exposure
1. "Lie straight on the table"
2. "Turn the affected leg slightly inward"
3. "Keep the other leg apart"
4. "Do not move during the exposure"
5. "Hold your position until told"